Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
小山 知弘*; 家田 淳一; 千葉 大地*
Applied Physics Letters, 116(9), p.092405_1 - 092405_5, 2020/03
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:25.92(Physics, Applied)The electric field (EF) modulation of magnetic domain wall (DW) creep velocity  in Pt/Co/Pd structure with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (MA) has been studied. The structures with different Co thickness
in Pt/Co/Pd structure with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (MA) has been studied. The structures with different Co thickness 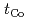 up to
up to 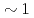 nm are investigated. In all samples, applying a gate voltage induces a clear change in
nm are investigated. In all samples, applying a gate voltage induces a clear change in  . Thicker samples provide a higher
. Thicker samples provide a higher  modulation efficiency, and the
modulation efficiency, and the  modulation magnitude of more than a factor of 100 times is observed in the thickest
modulation magnitude of more than a factor of 100 times is observed in the thickest 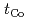 of 0.98 nm. The parameter characterizing the creep motion is significantly affected by the EF, resulting in the modulation of
of 0.98 nm. The parameter characterizing the creep motion is significantly affected by the EF, resulting in the modulation of  . Unlike the
. Unlike the  case, the MA modulation efficiency decreases with increasing
case, the MA modulation efficiency decreases with increasing 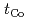 . The present results are discussed based on the EF-induced change in the interfacial Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction (iDMI), which has been recently demonstrated in the same structure, and
. The present results are discussed based on the EF-induced change in the interfacial Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction (iDMI), which has been recently demonstrated in the same structure, and 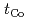 dependence of the DW energy. The
dependence of the DW energy. The 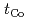 dependence of the
dependence of the  modulation suggests that the EF effect on the iDMI is more important than the MA.
modulation suggests that the EF effect on the iDMI is more important than the MA.
小山 知弘*; 仲谷 栄伸*; 家田 淳一; 千葉 大地*
Science Advances (Internet), 4(12), p.eaav0265_1 - eaav0265_5, 2018/12
被引用回数:50 パーセンタイル:88.54(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Pt/Co/Pd非対称構造において電場が磁壁速度を制御できることを示す。ゲート電圧を印加すると、50m/sまでの磁壁速度の著しい変化が観察され、これは以前の研究で観察されたものよりはるかに大きい。さらに、100m/sを超える磁壁速度の明確な変調も確認した。電場による界面のDzyaloshinskii-Moriya相互作用(DMI)の数パーセントまでの変化が、速度変調の原因であることがわかった。ここに示されているDMIを介した速度変化は、電場による異方性変調によって引き起こされるものとは根本的に異なるメカニズムである。本結果は、スピントロニクスデバイスの性能を向上させることができるDMI制御によるスピン構造とダイナミクスの電気的操作への道を開くものである。
家田 淳一; 山根 結太*; Sinova, J.*
no journal, ,
近年、反強磁性体を舞台としたスピントロニクス現象に注目が集まっている。特に、反強磁性ダイナミクスの電気的制御と検出という観点から、スピントルクやスピン起電力など、これまで強磁性体において確立し主要な役割を担っていた概念の再検討が重要な課題となる。理論的にも既にいくつかのアプローチが提案されているが、未だ十分なコンセンサスが得られてはいない。本研究では、反強磁性磁気構造のダイナミクスによるスピン起電力を理論的に検討する。先行研究において考慮されていなかった、副格子磁化の傾角性(有限の磁化の存在)、電子スピンと副格子磁化の交換相互作用における非断熱性、ラシュバスピン軌道相互作用の効果を取り込む。磁壁磁場駆動と反強磁性共鳴を具体的に取り上げ反強磁性単体から電圧生成が可能であることを示す。これらは反強磁性ダイナミクスの電気的な検出方法を与えるものとして有益であり、スピン起電力の出力増大に向けた物質探索の可能性を広げるものでもある。
佐藤 奈々; Schultheiss, K.*; K rber, L.*; Puwenberg, N.*; M
rber, L.*; Puwenberg, N.*; M hl, T.*; Awad, A. A.*; Arekapudi, S. S. P. K.*; Hellwig, O.*; Fassbender, J.*; Schultheiss, H.*
hl, T.*; Awad, A. A.*; Arekapudi, S. S. P. K.*; Hellwig, O.*; Fassbender, J.*; Schultheiss, H.*
no journal, ,
In the last decade, two revolutionary concepts in nano magnetism emerged from research for advanced information processing and storage technologies. The first suggests the use of magnetic domain walls (DWs) in ferromagnetic nanowires to permanently store information in DW racetrack memories. The second proposes a hardware realisation of neuromorphic computing in nanomagnets using nonlinear magnetic oscillations in the GHz range. Both ideas originate from the transfer of angular momentum from conduction electrons to localised spins in ferromagnets, either to push data encoded in DWs along nanowires or to sustain magnetic oscillations in artificial neurones. Even though both concepts share a common ground, they live on very different time scales which rendered them incompatible so far. Here, we bridge both ideas by demonstrating the excitation of magnetic auto-oscillations inside nano-scale DWs using pure spin currents.